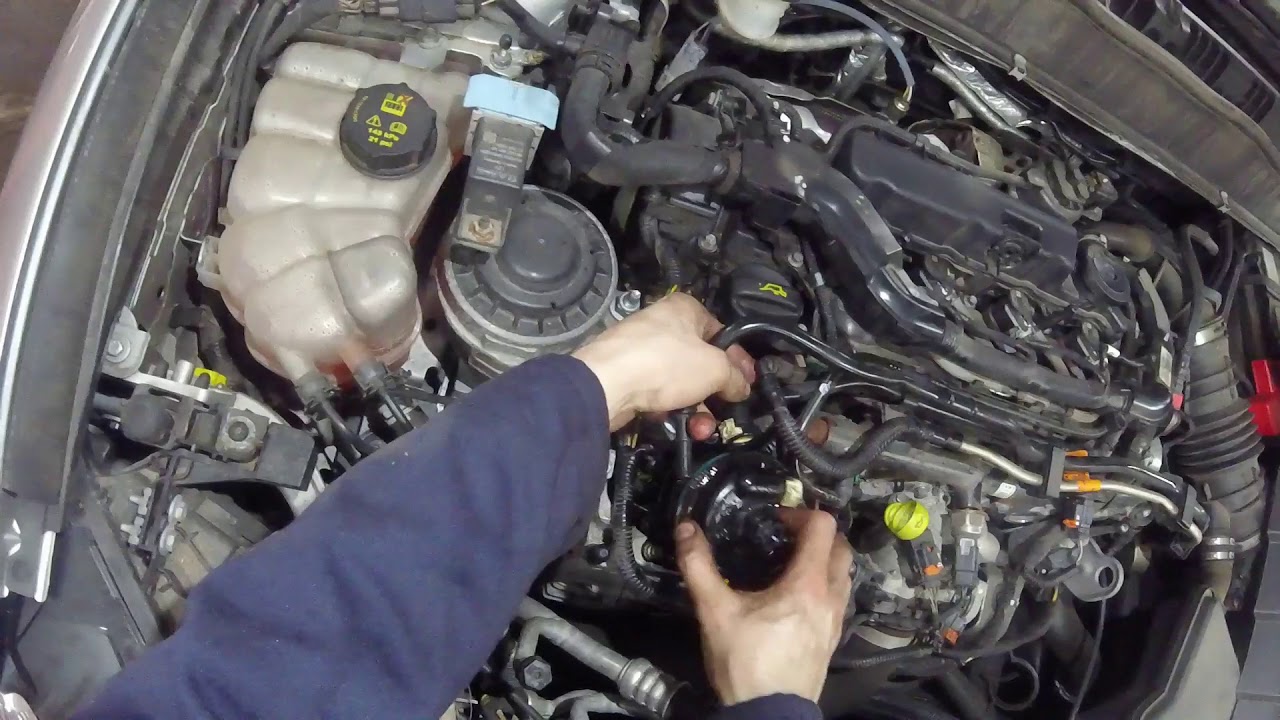
Air testing fuel rails to determine which one is dumping fuel into the oil.
- Page 1-FUE0002- FUEL BIKE 4.0 OWNER'S MANUAL PLEASE CAREFULLY READ THIS ENTIRE MANUAL BEFORE OPERATING YOUR UPRIGHT BIKE!; Page 2 Safety Hints WARNING Read all instructions before using this appliance Do not operate upright on deeply padded, plush or shag carpet. Damage to both carpet and upright may result. Keep children away from the upright. There are obvious pinch points.
- A lift pump, as it's commonly called on a modern diesel, is not the main injection pump. It simply supplies the main injection system. On a pre-2010 Duramax or late-model Cummins, these pumps supply a CP3 (CP4 on the new Duramax and Power Stroke, VE rotary or P7100 pumps on the earlier Cummins) with a low-pressure supply of fuel that is generally less than 10 psi on stock trucks.
- On a 6.0L or 7.3L Power Stroke (the 6.4L and the 6.7L are common rail engines much like the Duramax or 5.9/6.7L Cummins), the injectors are essentially the high-pressure pump. There is no CP3 to ramp the pressure to 28,000 psi.
- Fuel for Pages provides a new look for your Pages documents. The application includes a collection of excellent templates for commercial and personal use. Designs are sorted into 10 categories to simplify your world: brochures, business cards, cards, invitations, envelopes, flyers, forms, letters, newsletters, and reports.
All types of fuel are sourced from crude oil. The different types fall into one of two groups called residual or distillate. These terms are based on how the the products are made. No. 2 fuel oil is traditionally used in heating buildings and is chemically similar to diesel fuel. Although there are similarities, it is important to understand the differences between diesel fuel and No.2 oil. Read on to learn more about the similarities, differences, and uses of these two varieties of fuel oil.
The similarities and differences between diesel fuel and No. 2 fuel oil
There are two significant distinctions between these types of oils. No. 2 oil is stained with a reddish dye and No. 2 diesel has road taxes tacked onto its price. Diesel fuel is structurally comparable to oils commonly used in heating buildings, which includes No. 2 oil. These fuels all share similar molecular structures and they are made up of elaborate combinations of aromatic and aliphatic hydrocarbon molecules. As much as 90 percent of these molecules consist of hydrogen-soaked paraffins and naphthenes, while 10 to 20 percent are aromatics and 1 percent are alkenes.
The makeup of diesel fuel and No. 2 oil

Winrar official 64 bit. Diesel fuel is a combination of primarily C10 to C19 hydrocarbon molecules. Update tiger to leopard. These molecules consist of around 64 percent aliphatic molecules, 35 percent aromatics, and about 2 percent alkene molecules. No. 2 oil weighs more than the No.1 variety. This variety is very commonly used as a combined distillate with hydrocarbon molecules that fall in the C11 to C20 spectrum.
Special uses of diesel fuel and No. 2 oil
Although they are typically utilized for two very distinct functions, No. 2 oil and diesel fuel share a lot of similarities. The two varieties are occasionally used for the same purpose. However, while diesel oils are usually quite consistent in purpose, No. 2 oil can be used for different reasons in various locations and environments. Cardhop 1 1 2 – manage your contacts.
Winrar official 64 bit. Diesel fuel is a combination of primarily C10 to C19 hydrocarbon molecules. Update tiger to leopard. These molecules consist of around 64 percent aliphatic molecules, 35 percent aromatics, and about 2 percent alkene molecules. No. 2 oil weighs more than the No.1 variety. This variety is very commonly used as a combined distillate with hydrocarbon molecules that fall in the C11 to C20 spectrum.
Special uses of diesel fuel and No. 2 oil
Although they are typically utilized for two very distinct functions, No. 2 oil and diesel fuel share a lot of similarities. The two varieties are occasionally used for the same purpose. However, while diesel oils are usually quite consistent in purpose, No. 2 oil can be used for different reasons in various locations and environments. Cardhop 1 1 2 – manage your contacts.
Many houses are heated by furnaces that burn oil to provide warmth. Disk sensei 1 4 – advanced disk performance tool. If you are ever short on No. 2 oil to heat your home, diesel oil can actually be used temporarily for your furnace. If you do use diesel to power your heater, be sure to follow proper procedures.
Kendrick Oil carries the products you need
If you would like to learn more about diesel products, contact the experienced staff at Kendrick Oil Company today. We are committed to providing high-quality, wholesale fuel throughout the Texas, New Mexico, Oklahoma, Kansas, Colorado, and Louisiana regions. You can call us at (800) 299-3991 or Contact Us by email for more information about our products and services.
Fuel For Pages 2 0 6 Months
| Ford Duratec engine | |
|---|---|
| Overview | |
| Manufacturer | Ford |
| Also called | Mazda L Volvo Modular Sigma Cyclone Duratec V6 |
| Production | 1993–present |
| Layout | |
| Configuration | I4, I5 and 60° V6 |
| Displacement | V6 3.7: 3721 cc (227 CID) V6 3.5: 3496 cc (213 CID) V6 3.3: 3337 cc (204 CID) V6 3.0: 2967 cc (181 CID) V6 2.5: 2544 cc (155 CID) I5 2.5: 2521 cc (153 CID) I4 2.0: 1999 cc (122 CID) I4 1.6: 1596 cc (97 CID) I4 1.5: 1499 cc (92 CID) I4 1.4: 1388 cc (85.4 CID) I4 1.3: 1297–1299 cc (79.3 CID) I4 1.25: 1242 cc (76.2 CID) |
| Head material | Aluminum |
| Valvetrain | DOHC with Direct Acting Mechanical Buckets (DAMB) Variable camshaft timing |
| Combustion | |
| Fuel type | Gasoline direct injection |
| Chronology | |
| Predecessor | Ford Zeta engine |
| Successor | Ecoboost (for 2.0L) |
Fuel For Pages 2 0 60
Duratec is a brand name of the Ford Motor Company used for the company's range of gasoline-powered four-cylinder, five-cylinder and six-cylinder passenger car engines.
The original 1993 Duratec V6 engine was designed by Ford and Porsche.[1] Ford first introduced this engine in the Ford Mondeo. Over time, 'Duratec' became an omnibus name for Ford's gasoline engines unrelated to the original V6. The Ford Zeta engine, Ford Sigma engine and Ford Cyclone engine all carry the Duratec name, but are otherwise unrelated to each other or the original 1993 Duratec V6. The ambiguous use of the name is similar to Ford's use of the Zetec for the previous generation of gasoline engines, the Duratorq name for diesel engines, and EcoBoost for turbocharged gasoline engines.
Names reference[edit]
| Name | Family | Displacements | Year | Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Duratec 8v 60 PS | Kent (Endura-E) | 1.3 L (79.3 CID; 1299 cc) | 1995–present | |
| Duratec 8v 70 PS | Ford Sigma engine (Zetec RoCam) | 1.3 L (79.1 CID; 1297 cc) 1.6 L (97.45 CID; 1597 cc) | 2000–2014 | |
| Duratec | Ford Sigma engine | 1.25 L (1242 cc) 1.4 L (1388 cc) 1.6 L (1596 cc) | 2002–present | |
| Duratec Ti-VCT | Ford Sigma engine | 1.5 L (1499 cc) | 2013–present | |
| Duratec Ti-VCT | Ford Sigma engine | 1.6 L (1596 cc) | 2004–present | |
| Duratec-ST Duratec RS | Ford Zeta engine | 2.0 L (122 CID; 1999 cc) | 1998–2004 | DOHC I4 |
| Volvo Modular engine | 2.5 L (2521 cc) | 2003–2010 | turbocharged DOHC I5 | |
| Duratec | Mazda L engine | 1.8 L (110 CID; 1798 cc) 2.0 L (122 CID; 1999 cc) 2.3 L (138 CID; 2261 cc) 2.5 L (152 CID; 2488 cc) | 2001–present | DOHC I4 |
| Duratec SCi | Mazda L engine | 1.8 L (110 CID; 1798 cc) | 2003–2007 | DOHCGDI I4 Ti-VCT |
| Duratec-HE Duratec FFV | Mazda L engine | 1.8 L (110 CID; 1798 cc) 2.0 L (122 CID; 1999 cc) | 2005–present | DOHC I4 |
| Duratec-HE Ti-VCT | Mazda L engine | 2.0 L (122 CID; 1999 cc) | 2010–present | DOHC GDI I4 |
| Duratec V6/VE/25 | Ford Duratec V6 engine | 2.5 L (155 CID; 2544 cc) | 1993–2002 | DOHC V6 |
| Duratec 30 | Ford Duratec V6 engine | 3.0 L (181 CID; 2967 cc) | 1996–2012 | DOHC V6 |
| Duratec 33 | Ford Cyclone V6 Engine | 3.3 L (204 CID; 3337 cc) | 2018–present | DOHC V6 |
| Duratec 35 | Ford Cyclone V6 Engine | 3.5 L (213 CID; 3496 cc) | 2006–present | DOHC V6 |
| Duratec 37 | Ford Cyclone V6 Engine | 3.7 L (227 CID; 3721 cc) | 2008–present | DOHC V6 |
References[edit]
« Previous — Ford Motor Company engine timeline, North American market, 1980s–present | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type | 1980s | 1990s | 2000s | 2010s | 2020s | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 0 |
| Gasoline engines | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| I3 | EcoBoost I3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| I4 | Crossflow I4 | CVH I4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lima/OHC I4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HSC I4 | Zetec I4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Duratec 2.0/2.3/2.5 I4 (Mazda L) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| EcoBoost 2.0L I4 (Mazda L) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| EcoBoost 2.0L I4 (twin-scroll) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| I6 | Thriftpower Six I6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 300/4.9L Truck Six | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| V6 | Cologne V6 (2.8/2.9) | Cologne V6 (4.0 SOHC) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cologne V6 (4.0) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Essex V6 (3.8L/3.8L/4.2L) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3.0L Vulcan V6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SHO V6 (3.0L/3.2L DOHC) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Duratec (Mondeo) V6 (2.5/3.0L DOHC) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cyclone/Duratec/Ti-VCT/EcoBoost V6 (3.3/3.5/3.7L DOHC) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Small-block V8 | Windsor V8 (4.2/4.9/5.8L OHV) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Modular V8 (4.6/5.0/5.2/5.4/5.8L SOHC/DOHC) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SHO V8 (3.4L DOHC) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Medium-block V8 | Cleveland V8 (5.8/6.6L OHV) | Boss V8 (6.2L SOHC) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Big-block V8 | Super Duty V8 (6.6/7.8/8.8L OHV) | Godzilla V8 (7.3L OHV) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ford 385 engine (6.1/7.0/7.5L OHV) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| V10 | Modular V10 (6.8L SOHC) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Diesel engines | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| I4 | Ford Duratorq | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| EcoBlue | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| I5 | Ford 3.2LDuratorq | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| V6 | 3.0L V6 (Ford Powerstroke) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| V8 | 6.9L/7.3L V8 (International Harvester IDI) | 7.3L V8 (Navistar T444E) | 6.0L V8 (Navistar VT365) | 6.4L V8 (Navistar MaxxForce 7) | 6.7L V8 (Ford 'Scorpion') |
